Quality assurance teams spend up to 40% of their time maintaining broken test scripts—a staggering inefficiency that plagues modern software development. Throughout my experience implementing test automation across multiple projects, I’ve witnessed teams dedicate entire sprints to fixing tests that failed due to minor UI changes rather than focusing on identifying actual bugs.
Traditional automation tools promise efficiency but often deliver maintenance nightmares instead. However, teams leveraging AI-powered test automation platforms like Testim have reported remarkable improvements: up to 70% reduction in maintenance overhead and an 85% decrease in flaky test failures.
This shift represents more than just incremental improvement—it’s a fundamental transformation in how we approach test automation.
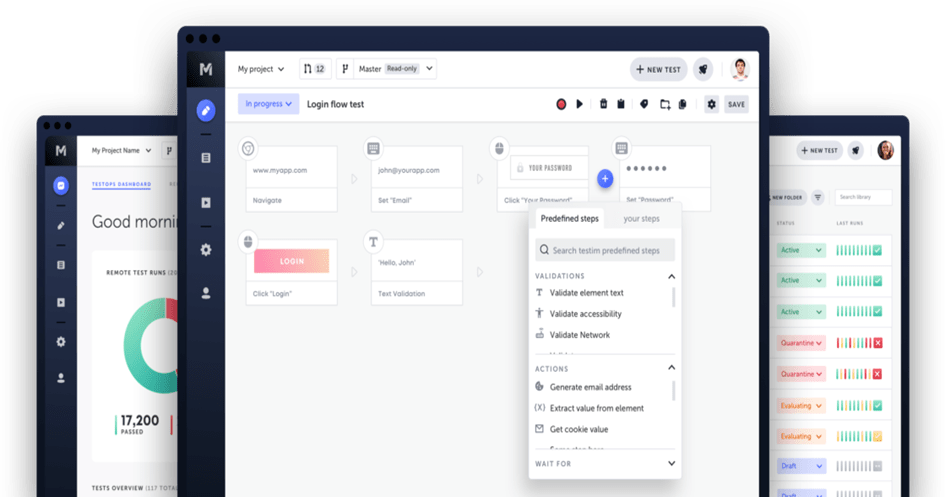
What is Testim?
Testim is a cloud-based test automation platform that leverages artificial intelligence to simplify test creation and dramatically reduce maintenance overhead. Unlike traditional tools that rely solely on XPath or CSS selectors, Testim employs Smart Locators that track multiple attributes of an element and automatically adjust when the UI undergoes changes.
During a recent project, I implemented Testim to automate regression tests for a web application that experienced frequent UI updates. The Smart Locator feature eliminated the need to repeatedly fix scripts when minor UI tweaks were deployed, saving countless hours of maintenance work.
The platform supports low-code test authoring, cross-browser test execution, and parallel test runs. It seamlessly integrates with development pipelines and version control systems, making it effortless to embed into existing workflows.
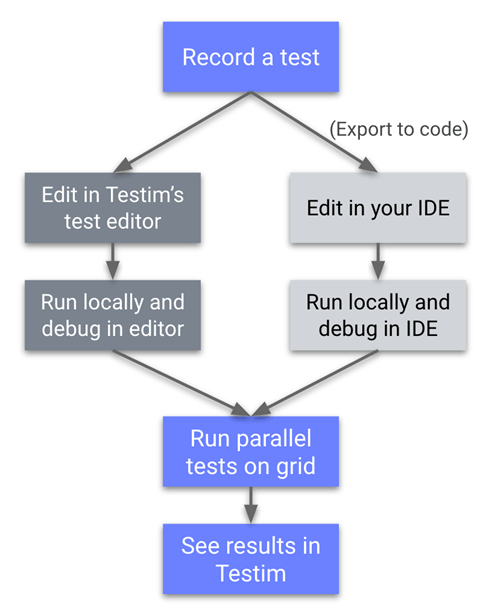
Test Automation Workflow in Testim
Key Features of Testim
During my initial adoption of Testim, several features immediately addressed long standing challenges I had encountered with traditional automation tools. These weren’t just innovative in theory, they provided practical solutions to recurring problems in real-world testing environments. The following capabilities had the most significant impact on our testing workflows:
1. AI-Powered Smart Locators
Tired of flaky tests breaking over tiny UI changes? That’s test brittleness – a major automation headache. Testim’s Smart Locators tackle this using AI to analyze multiple element properties at once (like text, IDs, position, and nearby elements). The result? More stable tests that rarely break during routine updates. While not foolproof (major element overhauls may need tweaks), this approach dramatically cuts maintenance time by automatically adapting to most UI shifts.
2. Low-Code/No-Code Interface
This automation framework strikes an optimal balance between accessibility and flexibility. The drag-and-drop interface enables rapid test creation for standard scenarios like form validation and authentication flows, while custom JavaScript integration handles complex dynamic behaviors and conditional logic. This dual approach accommodates both technical and non-technical team members.
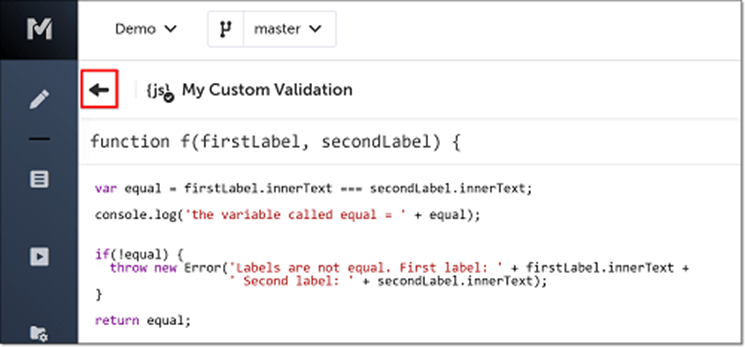
Example for JavaScript code
3. Visual Test Editor
The platform’s intuitive visual editor allows users to record, modify, and enhance test steps without coding. Users can easily incorporate validations, conditional statements, and iterative loops to build comprehensive test scenarios that mirror real user journeys.
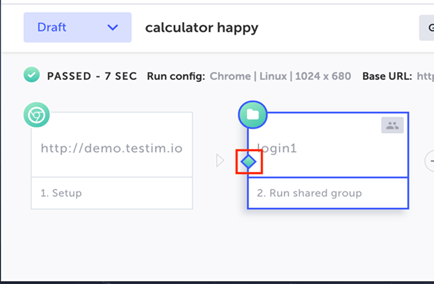
Example for a Condition
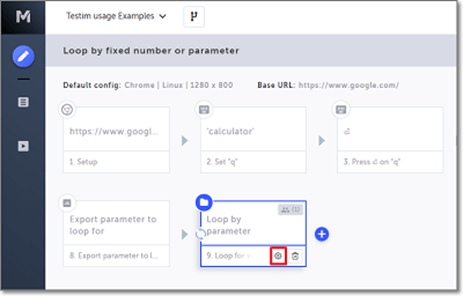
Example for a Loop
4. Cross-Browser and Mobile Testing
The platform supports testing across multiple browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge) and various device configurations. This comprehensive coverage helps identify environment-specific issues that might otherwise reach production, ensuring consistent user experiences across different platforms.
5. Parallel Execution
Parallel test execution dramatically reduces feedback time in CI/CD pipelines and is a critical capability for maintaining development velocity. By distributing test loads across multiple execution threads, teams can identify issues earlier without creating bottlenecks in the release process.
6. Version Control Integration
Native Git integration allows teams to manage test assets with the same rigor as production code. This ensures proper collaboration, maintains audit trails, and enables rollback capabilities for test scripts.
Key Advantages
Testim offers a host of benefits that make it highly effective for test automation:
| Time Efficiency The tool’s AI-driven approach minimizes the time spent on test creation and maintenance, freeing up teams to focus on building features | Reduced Unreliability Smart locators ensure tests remain stable even as the application evolves, reducing false negatives and flaky tests | Seamless Integrations The platform integrates effortlessly with popular CI/CD tools like Jenkins, CircleCI, and GitLab, making it easy to incorporate into existing workflows |
Accessibility With its low-code interface, Testim is accessible to a wide range of team members, from QA engineers to developers and business analysts | Scalability This automation solution is designed to scale with your team, whether youʼre a small startup or a large enterprise |
Implementation Challenges to Consider
While Testim offers significant advantages, it’s important to acknowledge the practical challenges teams may face during adoption:
1. Initial Learning Curve for Complex Scenarios
Although the platform offers a low-code interface, building advanced scenarios using JavaScript, conditions, or dynamic elements may require technical expertise. Teams new to automated testing may need additional training and support.
2. Limited Native Mobile App Testing
Compared to tools specifically built for mobile testing, Testim’s capabilities for native mobile app testing are somewhat limited. Teams may need to integrate additional tools like Appium for comprehensive mobile test coverage.
3. Cost Considerations and Vendor Dependencies
As a proprietary solution, migrating existing test suites from or to Testim can be challenging. Pricing may also be a consideration for small startups or teams with limited QA budgets.
4. Performance Considerations at Scale
In large-scale test suites with numerous parallel threads, some teams may experience performance bottlenecks, especially when executing complex test logic or managing frequent updates.
5. Smaller Community Ecosystem
Unlike open-source tools such as Selenium or Cypress, Testim has a smaller community ecosystem. This can mean fewer tutorials, plugins, or community-driven solutions available.
How to get started with Testim
Testim is designed to seamlessly integrate into modern software testing workflows. Its intuitive interface and intelligent automation capabilities streamline test creation, execution, and analysis. The following steps outline its core functionality:
1. Test Recording
Testim captures interactions as the user navigates the application, automatically generating the foundational steps for each test case. This eliminates the need for manual scripting while ensuring high fidelity to real-world user flows.
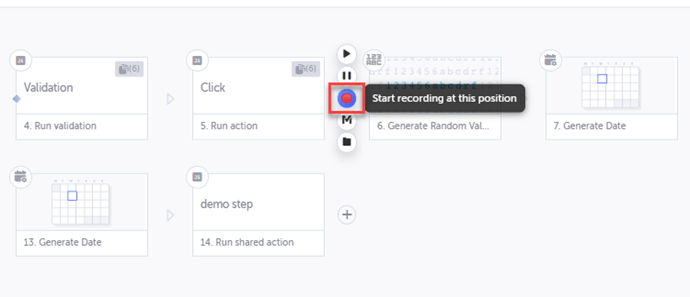
2. Test Editing and Enhancement
Using the visual editor, teams can refine recorded steps by adding assertions, loops, and conditional logic. This enables the creation of robust test scenarios that address both typical use cases and critical edge conditions.
3. Test Execution
Tests can be executed locally or in cloud-based environments, supporting multiple browsers and device configurations. Each test run is accompanied by detailed diagnostics, including logs, screenshots, and video recordings, which accelerate root cause analysis in case of failures.
4. Result Analysis and Reporting
Execution results are presented in a centralized dashboard, offering actionable insights into pass/fail outcomes, failure trends, and flaky tests. This allows teams to prioritize defect resolution and maintain the reliability of their automation suite.
Best Practices for Success
To fully leverage Testim’s capabilities and establish a scalable, maintainable test automation strategy, adopt these proven practices:
1. Strategic Smart Locator Customization
While Testim’s AI-based Smart Locators effectively reduce brittleness, stability can be enhanced by introducing custom attributes like data-testid for key elements. In one implementation, assigning stable identifiers to the checkout module eliminated repeated test failures that had persisted across multiple release cycles.
2. Modular Test Design
Structure tests as modular components representing common flows (login, cart interactions, form validation). When business logic changes, updates can be made in a single shared module rather than across multiple scripts—ensuring consistency and minimizing rework.
3. Apply Development Standards to Test Assets
Treat automation artifacts with the same rigor as application code. Store tests in version control systems (Git), enforce peer reviews, and maintain documentation for complex logic. This fosters collaboration and ensures traceability, especially in large or distributed teams.
4. Implement Incremental Validation Throughout Test Flows
Insert assertions at key checkpoints throughout test flows rather than validating only at the end. This approach facilitates earlier fault detection and provides more granular insight into failure points—making diagnosis faster and more precise.
5. Optimize Parallel Test Execution
Group independent test cases for concurrent execution to reduce CI/CD pipeline feedback time. Prioritize high-value smoke tests early in the execution sequence to identify critical issues with minimal delay.
6. Establish Clear Naming Conventions
Use descriptive, standardized naming patterns that reflect test intent. Clear names improve readability, maintainability, and reporting clarity.
Examples: Use Login_ValidUser_Success instead of ambiguous labels like Test1 or Scenario_A
7. Maintain Regular Test Hygiene
Establish a cadence for reviewing and optimizing test suites. Remove redundant or obsolete test cases, update outdated flows, and refactor complex logic into smaller, maintainable components. This reduces technical debt and improves reliability over time.
8. Integrate Multiple Testing Layers
Complement UI validations with API-level checks within the same test flow. This dual-layer approach enhances test coverage and helps pinpoint whether failures originate in frontend interactions or backend services.
Competitive Analysis: Testim vs Other Automation Tools
Testim’s AI-powered smart locators, low-code interface, and maintenance efficiency make it a compelling choice for teams seeking to optimize resources without compromising quality:
| Feature / Tool | Testim | Selenium | Cypress | Playwright |
| Smart Locators | AI self-healing | Manual | Static locators | Auto-retry only |
| Learning Curve | Low (1–2 days) | High (1–2 weeks) | Medium (3–5 days) | Medium (3–5 days) |
| Ease of Use | Low-code interface | Code-based | Code-based | Code-based |
| CI/CD Integration | Built-in cloud grid | Custom infrastructure | Built-in | Built-in |
| Cross-Browser Support | Full | Limited | Limited | Full |
| Parallel Execution | Built-in | Manual setup | Built-in | Built-in |
| API Testing Support | Native | Needs external tools | Built-in | Strong |
| Mobile Testing | Limited | With Appium | No | With Appium |
| Performance Optimization | AI-based | Manual tuning | Limited parallelism | Fast & scalable |
| Cost of Ownership | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Low |
Future Trends in Test Automation
As software development lifecycles accelerate and systems grow in complexity, test automation must evolve to remain effective. Testim is actively shaping the future of quality engineering through these emerging trends:
1. Self-Healing Test Architecture
Flaky tests—those that fail due to UI or DOM changes rather than functional issues—remain a critical challenge in automated testing. Self-healing capabilities use AI to detect and respond to such changes by dynamically adjusting element selectors during test execution.
Use Case: When a “Submit” button’s ID or location changes, traditional tests may break. In contrast, Testim’s AI-powered Smart Locators evaluate multiple attributes, allowing the test to proceed reliably without manual intervention.
2. Autonomous Test Generation
The future of automation involves minimizing manual test creation. Autonomous testing solutions aim to generate tests by analyzing user behavior, logs, and application usage patterns.
Testim is advancing in this area by:
- Recommending test flows based on application structure and user interactions
- Learning from recurring patterns to suggest reusable components
- Laying the groundwork for automatic regression suite creation based on real user paths
These capabilities help teams extend test coverage while reducing the manual effort required to build test suites.
3. Shift-Left Testing Integration
“Shift-left” emphasizes integrating testing earlier in the software development lifecycle. This reduces feedback latency and improves product quality before code reaches production.
Testim supports shift-left practices through:
- A low-code/no-code interface that enables collaboration among developers, testers, and business stakeholders
- Git integration, allowing tests to be version-controlled alongside application code
- Compatibility with CI/CD pipelines, facilitating early and automated validation
This approach fosters continuous quality and aligns QA with agile delivery principles.
4. Integrated Quality Intelligence
Future-ready testing frameworks extend beyond pass/fail outputs by delivering actionable insights through quality analytics. Integrated quality intelligence includes:
- Historical trend analysis of test runs
- Identification of unstable or frequently failing tests
- Predictive alerts for potential breakpoints based on previous failures
Testim is enhancing its dashboard capabilities to deliver such insights, helping teams prioritize stability and make informed decisions based on data.
5. Unified Testing Ecosystem
Modern applications require validation beyond the user interface. Testing must encompass backend APIs and performance under varying load conditions.
While Testim is primarily focused on UI testing, it is actively expanding support to:
- Incorporate API validation within functional UI tests
- Enable hybrid testing workflows that validate frontend behavior and backend logic in a single execution
- Explore integrations for performance metrics such as response time and resource utilization
This unified approach ensures broader coverage across the entire application stack.
Conclusion
This exploration of Testim wasn’t about proving one tool superior to others—it was about learning through direct implementation. In my experience using Testim in a real-world QA environment, the platform successfully reduced repetitive maintenance effort and improved test reliability. However, like any tool, it comes with trade-offs that must be carefully evaluated.
If you’re considering AI-based test automation, I recommend evaluating options based on your team’s specific needs and development setup. While my experience may not apply universally, I hope it provides valuable reference points for others embarking on their automation journey.
The future of test automation lies in intelligent, self-adapting systems that reduce manual overhead while increasing test reliability. Testim represents a significant step toward this vision, offering teams a practical path to more efficient and maintainable test automation.
